Art is not produced by nature but manmade. In mathematics or the laws of physics, there is merely discovering what is already there. But a piece of artwork has the application of human imagination and perceived differently by individuals. Art is thus subjective when it comes to liking by an audience.
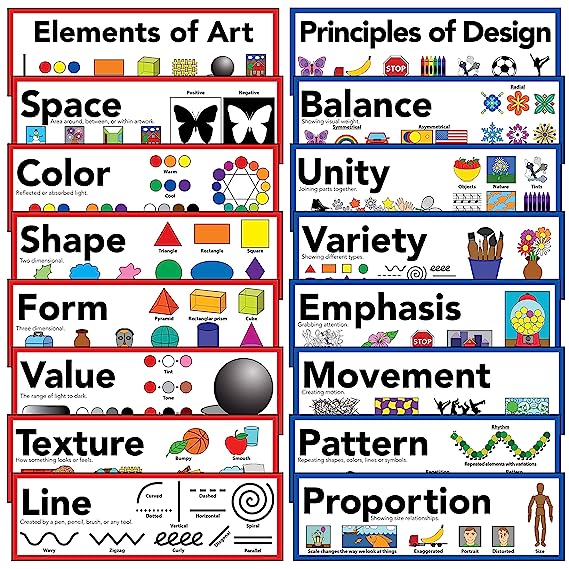
Elements of visual art are building blocks artists use to design their work. Formal elements are space, point, line, shape, color, value (light and dark), and texture. Using these as bricks, an artist creates a whole new world of visual experience. While designing artwork, an artist selects his or her theme of dominance called ‘emphasis.’ To make artwork pleasant, visual combinations are used called building ‘harmony.’ ‘Unity of purpose’ is maintained while depicting elements so that all parts appear related. ‘Contrast’ such as using colors black and white in sequence makes the artwork more dramatic or expressive.
The artistic mind refers to the natural ability of an individual to learn skills such as painting or photography.
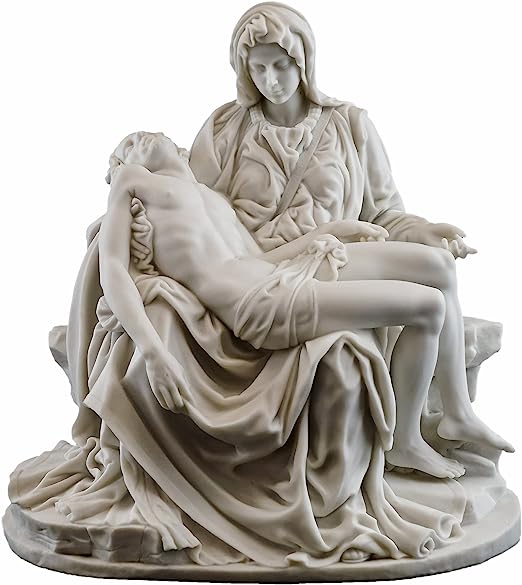
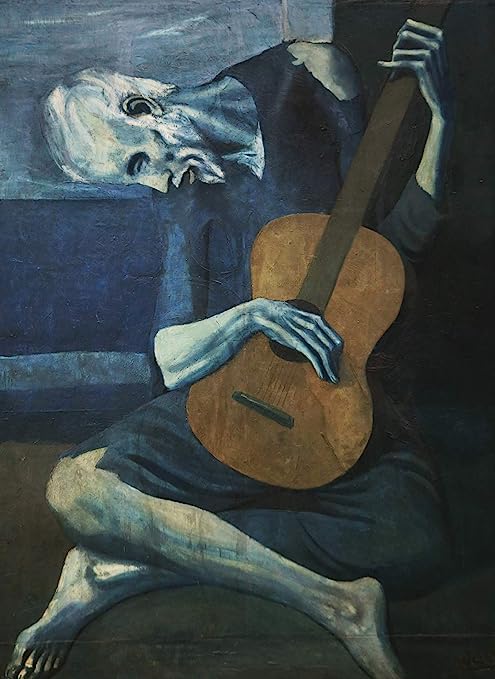
For some, it is easier to acquire artistic skills than others or are artistically talented. Painting of Mona Lisa by Leonardo da Vinci, sculptor of Pieta by Michelangelo, architectures such as The Hanging Gardens of Babylon and The Statue of Zeus at Olympia, printmaking such as Pablo Picasso’s The Old Guitarist are examples of popular visual arts.
Performing arts

Performing arts is when the individual perform separately or together with his body, face, or presence. Music, dance, and drama are examples. Magic is yet another performing art. What makes performing art part of visual art is ultimately say a dance performance by a dancer finds its way into images and videos consumed by the web audience of today the same way as works of visual arts.
Today, there is a flux of visual images around us, be it print or audio-video sources. Interpreting ideas conveyed by visible actions or images is called visual literacy. A picture, after all, is worth more than a thousand words.
National Geographic Magazine – Set of 2 Issues – Afghan Girl with Green Eyes – June 1985 Volume 167 Number 6 and April 2002 Volume 201 # 4 Paperback – 1985

Although beauty is one of the major objectives, bringing into notice the harshness of life is also frequently part of an artist’s work.
As per Adam Schwartz of TeePublic, “In times of human struggle, the world needs art. Crises such as this (Corona Virus) are too complex, too nuanced to put into words, but art is a higher form of language. When we don’t know what to feel, art can illustrate emotion … [As an artist] You do have a sword to wield. Can you push through the anxiety and find the space to be creative? Can you find your voice and whisper to us, a joke, an idea, or a memory of some better time? I implore you to try … as an artist community our voices echo more loudly than one could ever do alone.”
The human way of thinking rotates around rationality and imagination. While rationality relies on systematic learning by the effort of the brain and senses and applying to reason, imagination relies on intuition. The human body itself functions in two ways, some are automatic, such as the beating of the heart, and some are accomplished by active human endeavor such as walking. Similarly, our way of inner conception and outside communication is also guided by a combination of both.
While traditional classroom teaching relies more on rational means, still many times it has been found that people not having them have been able to succeed more in their fields by applying intuition and following hunches from their subconscious mind which is popularly called “psychic automatism.” From one angle, critical thinking and relying on hunches appear conflicting, but maybe, wisdom to balance the two can make the difference.
Throughout history, artistic works of excellence are always said to be achieved when its creator got in a trance state where he/she surrendered to the inner god or subconscious mind. The world’s best painters such as Picasso and Michelangelo, poets like Stevenson, and many more who do not disclose them publicly, have been able to achieve their masterpieces relying more on inner impulses of the soul free from reasoning than anything else.
In the modern digital age, such “psychic automatism” is increasingly being expressed in newer ways such as using computers where the artist selects buttons in a trance state and the output gets recorded on the monitor. Some call it like scribbling on paper in a half-dream state. In visual art, it has been practiced in religious imagery throughout human civilization.
During the last few decades, there has been renewed interest in understanding the power of the subconscious mind and artistic works under psychic automatism form find their place in commercial advertisements which is perhaps a good thing as the same brings pupils of commerce and arts streams together.
One of the challenges today in the world of marketing (digital marketing to be precise in the current web environment) is to woo customers by images/videos in websites, apps, and social media channels. It is going the extra mile to explore their relevant use that can give a competitive advantage.
2023 Update
Come 2023 and the ease with which AI tools like ChatGPT and Bard now allows generating images based on text prompts once again has opened new frontiers.
Visual art is a broad term that encompasses a wide range of creative expressions, including painting, sculpture, photography, and digital art. Generative AI is a type of artificial intelligence that can create new content, such as images, text, and music.
There are a number of ways in which visual art and generative AI can be applied to commerce. For example, generative AI can be used to create:
- Product images: Generative AI can be used to create high-quality product images that are more realistic and engaging than traditional stock photography. This can help businesses to sell more products online.
- Custom designs: Generative AI can be used to create custom designs for products, such as clothing, furniture, and home décor. This can help businesses to differentiate themselves from their competitors and attract new customers.
- Marketing materials: Generative AI can be used to create marketing materials, such as brochures, flyers, and social media posts. This can help businesses to reach a wider audience and promote their products or services.
In addition to these specific applications, generative AI can also be used to create more general visual content that can be used for a variety of purposes, such as:
- Backgrounds: Generative AI can be used to create realistic and engaging backgrounds for websites, presentations, and other projects.
- Icons: Generative AI can be used to create unique and memorable icons for websites, apps, and other products.
- Illustrations: Generative AI can be used to create illustrations for books, magazines, and other publications.
Overall, generative AI has the potential to revolutionize the way that visual art is used in commerce. By creating new and innovative ways to generate visual content, generative AI can help businesses to reach a wider audience, sell more products, and differentiate themselves from their competitors.
Here are some specific examples of how generative AI is being used in commerce today:
- IKEA: IKEA is using generative AI to create realistic 3D models of its furniture. These models can be used to help customers visualize how different pieces of furniture would look in their homes.
- Coca-Cola: Coca-Cola is using generative AI to create personalized marketing materials. The company’s AI can generate images, videos, and text that are tailored to the specific interests of each customer.
These are just a few examples of how generative AI is being used in commerce today. As the technology continues to develop, we can expect to see even more innovative and creative applications for visual art in the years to come.
Visual artists can leverage generative AI in various ways to enhance their creative process and create unique artworks. Here are some ways in which artists can use generative AI:
- Artistic Style Transfer: Generative AI algorithms can be used to transfer the style of one artwork onto another. Artists can use these algorithms to apply the style of famous artists or specific art movements to their own creations, resulting in visually striking and distinctive pieces.
- Creative Exploration: Generative AI models can generate random or semi-random outputs based on learned patterns and rules. Artists can use these outputs as a starting point for their own creative exploration. They can then modify and refine the generated content to match their artistic vision, using the generative AI as a source of inspiration and ideation.
- Procedural Generation: Generative AI can be employed to generate procedural elements of an artwork, such as textures, patterns, or compositions. Artists can define certain parameters and rules, and the AI model can generate variations based on those inputs. This approach allows artists to quickly explore a wide range of possibilities and iterate on their ideas.
- Interactive Art: Artists can create interactive installations or experiences using generative AI. By integrating AI models with sensors or other input devices, artists can enable viewers to interact with the artwork and have the AI generate real-time responses based on the input. This adds an element of unpredictability and engagement to the artistic experience.
- Collaborative Art: Artists can collaborate with generative AI models to co-create artworks. By training AI models on their own artistic style or previous works, artists can generate new content in collaboration with the AI. They can alternate between human and AI input, allowing the AI to suggest new elements or generate variations, which the artist can then refine and integrate into the final piece.
- Data Visualization: Generative AI can be used to visualize complex data sets in aesthetically pleasing and informative ways. Artists can leverage AI algorithms to transform raw data into visual representations that convey patterns, relationships, or narratives. This approach can help make data more accessible and engaging to a broader audience.
- Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR): Artists can leverage generative AI in AR and VR applications to create immersive and interactive virtual worlds. By combining AI-generated content with real-world environments or virtual spaces, artists can create unique digital experiences that merge the boundaries between physical and virtual art forms.
It’s important to note that while generative AI can be a powerful tool for artists, it should be seen as a tool to augment and inspire artistic creativity rather than replace it. The artist’s unique perspective, intention, and human touch remain essential in the creation of meaningful artworks.
Last Updated on June 13, 2023 by Rajeev Bagra



.jpg)
.jpg)












Leave a Reply